Consistency Test of Cement as per Indian Standard (IS 4031: Part 4)
Consistency Test of Cement
Aim
The aim of the consistency test is to determine the standard consistency of cement paste, which is the percentage of water required to produce a cement paste of standard consistency. This consistency is necessary to ensure that the cement has the right workability for further tests, such as setting time, compressive strength, and soundness.
Apparatus
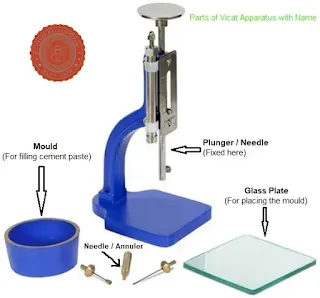
- Vicat Apparatus (with plunger of 10 mm diameter and 50 mm length)
- Weighing Balance
- Measuring Jar
- Glass Plate or Non-Absorbent Plate
- Trowel
- Cement Sample (around 500g)
- Water
Theory
The consistency of cement refers to the relative mobility or fluidity of the cement paste. The standard consistency is defined as the percentage of water that allows the Vicat plunger to penetrate a depth of 33-35 mm into a cement paste. It is an essential parameter that influences the setting time and strength of the cement. Consistency testing ensures that the correct amount of water is used in the preparation of cement for other tests like setting time, soundness, and strength tests.
The test is carried out by preparing a paste of cement and water and then determining the amount of water needed to allow the Vicat plunger to penetrate to a specified depth in a certain time frame.
Procedure
- Weigh Cement: Weigh 400g of cement.
- Add Water: Start with a water quantity of about 25% of the cement weight (i.e., 100 ml of water). Gradually add water and mix the cement thoroughly to form a paste.
- Fill the Vicat Mould: Place the cement paste in the Vicat mould resting on a glass plate. Fill the mould and level the surface without pressing hard.
- Position the Plunger: Place the mould under the Vicat apparatus and bring the plunger in contact with the surface of the cement paste.
- Release the Plunger: Release the plunger and allow it to penetrate the cement paste under its own weight.
- Measure Penetration Depth: Record the depth of penetration. The test is repeated by varying the water content until the plunger penetrates 33-35 mm from the top of the mould.
- Determine Water Content: The water content corresponding to this penetration is noted as the amount of water required for standard consistency.
Observation Table
| Trial No. | Weight of Cement (g) | Water Added (%) | Depth of Penetration (mm) | Consistency (Pass/Fail) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 400 | 25 | 20 | Fail |
| 2 | 400 | 26 | 28 | Fail |
| 3 | 400 | 27 | 34 | Pass |
Sample Readings
For instance, if 400g of cement is used, and the water content required to allow the plunger to penetrate 34 mm into the paste is 27% by weight, the result of the standard consistency of cement is reported as 27%.
Reporting the Results
- The standard consistency of cement is expressed as a percentage of the weight of cement used.
- The result is the percentage of water (by weight of cement) required to allow the Vicat plunger to penetrate to a depth of 33-35 mm from the top of the paste.
- For example, if the standard consistency is found to be 27%, it means that 27% of the weight of cement (108 ml of water for 400g cement) is the water content required for standard consistency.
Conclusion
The consistency of cement is critical for ensuring proper workability and strength development. Standard consistency is required for other tests like setting time, soundness, and compressive strength to ensure that the amount of water used is appropriate for a uniform mixture. Proper consistency ensures that the hydration of cement is optimal, and the setting and hardening processes will proceed as intended.





Comments
Post a Comment